Mole's screening - assess your moles with our Mole Atlas or come to the mole's check
Introducing the atlas of moles, created by us under the guidance of the famous Finnish dermatologist Prof. Raimo Suhonen.
We have divided moles into four groups: (1) benign moles, which are easily removed, (2) benign moles, which are difficult to remove with a good aesthetic result, (3) malignant skin changes or precancerous conditions, and (4) suspicious moles, requiring mandatory histological examination.
Angiokeratoma is a common, benign vascular formation. It can be removed using a radiofrequency knife. On the face, as a rule, there is usually no trace left after removal, on the body and limbs - only a light spot.
An atheroma is a benign cyst that forms as a result of the blockage of the sebaceous glands. Small atheromas can be removed with a radiofrequency knife. Usually, there is no trace left on the face after removal, only a light spot on the body and limbs. Large atheromas require removal through an incision, which is stitched up surgically. Such a procedure leaves a small scar.
Hemangioma is a common, benign vascular formation. It can be removed with a radiofrequency knife. On the face, there is usually no trace left after removal, on the body and limbs - only a light spot.
Dermatofibroma is a benign formation of connective tissue. It can disappear over time. It can be removed using a radiofrequency knife. On the face, there is usually no trace left after removal, on the body and limbs - only a light spot.
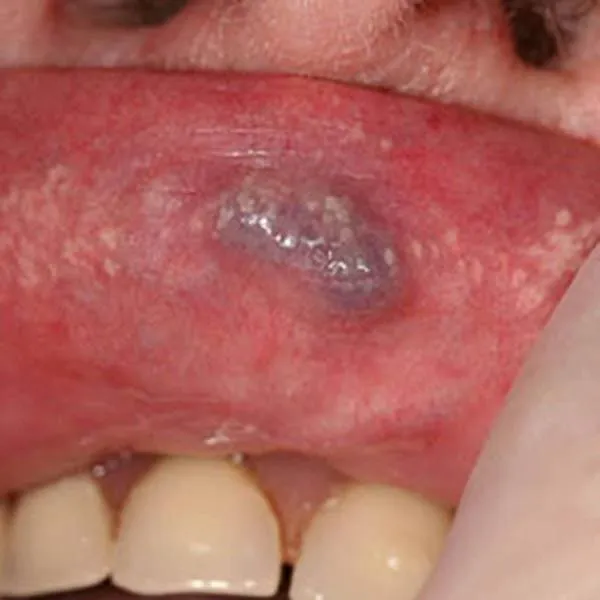
The photo shows yellowish spots of blocked sebaceous glands on the lips, the so-called Fordyce spots, and varicose vein enlargement. These formations can be removed using a radiofrequency knife. Traces rarely remain on the lips after removal.
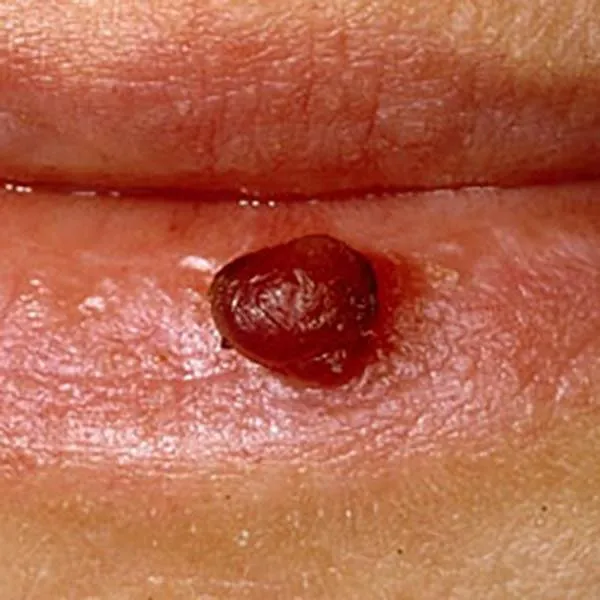
Pyogenic granuloma is a benign vascular formation that is prone to bleeding. It can be removed using a radio-frequency knife. On the face, usually, there is no trace left after removal, on the body and extremities - only a light spot.
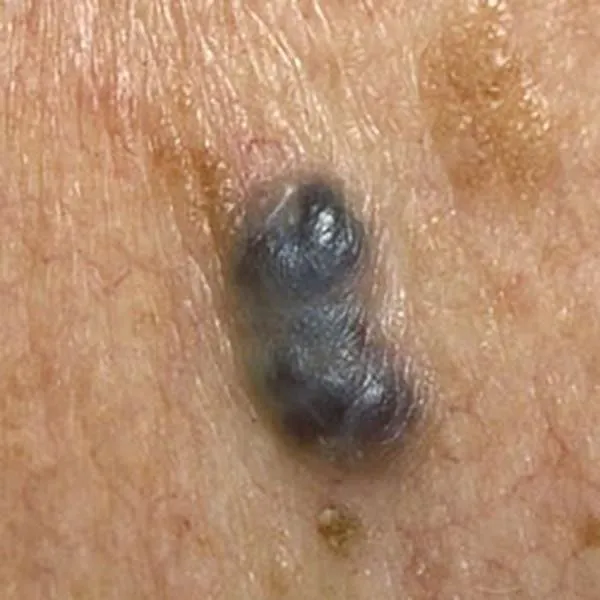
A hemangioma filled with venous blood that turns the mole black. When pressure is applied to the mole, it lightens because the blood leaves the mole. This serves as a diagnostic test. It can be removed using a radiofrequency knife. On the face, as a rule, there is no trace left after removal, on the body and limbs - just a light spot.
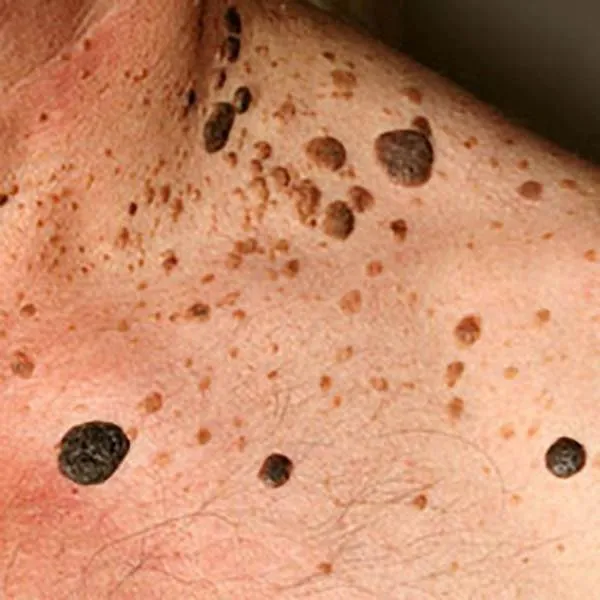
Seborrheic nevus is a benign skin formation that often itches. It can be removed using a radiofrequency knife. On the face, as a rule, there is no trace after removal, on the body and limbs - only a light spot.
Multicolored seborrheic nevus. It can be removed with a radiofrequency knife. On the face, as a rule, after removal there is no trace at all, on the body and limbs - only a light spot.
Multicolored seborrheic nevus. It can be removed using a radiofrequency knife. On the face, usually, there is no trace left after removal, on the body and limbs - only a light spot.
Multicolored seborrheic nevus. It can be removed using radiofrequency knife. After removal, there is usually no trace left on the face, and only a light spot remains on the body and limbs.
A benign, congenital, warty mole that does not degenerate into a malignant one. It can be removed with a radiofrequency knife. On the face, as a rule, there is no trace left after removal, on the body and limbs - only a light spot.
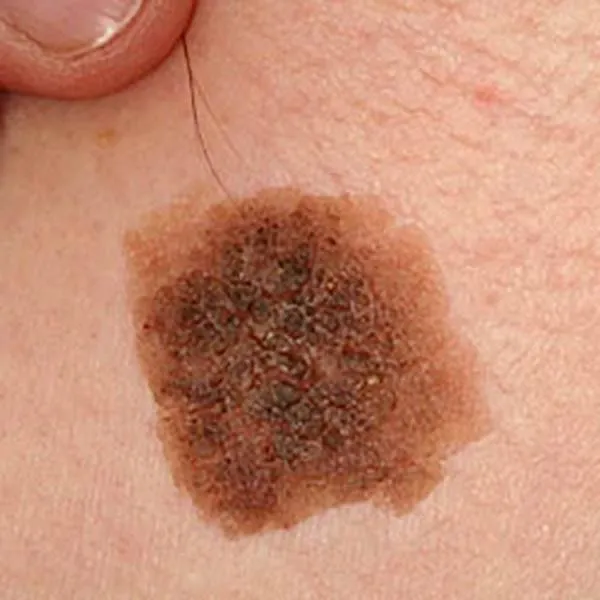
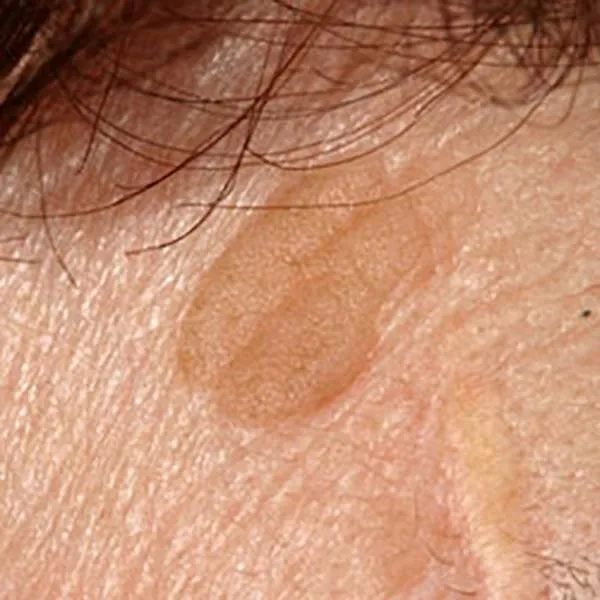
A typical seborrheic mole has a thick, rough surface with cracks. The tendency towards such moles is hereditary. They don't turn malignant. It can be removed with a radio frequency knife. On the face, as a rule, there is no trace left after removal, on the body and limbs - only a light spot.
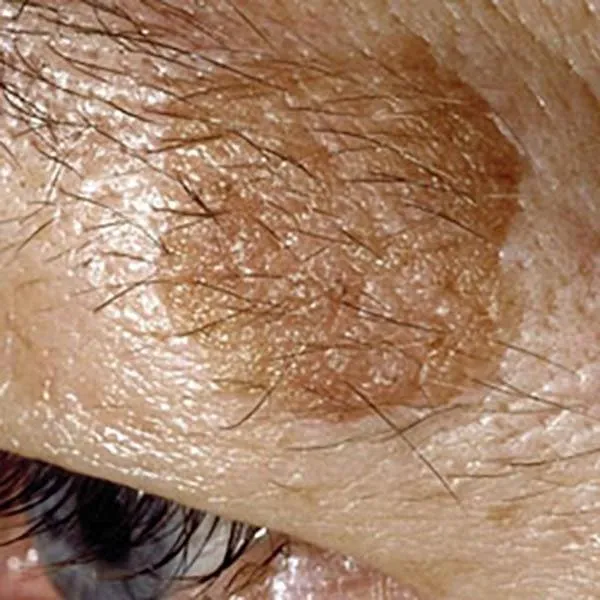
Flat seborrheic mole on the eyebrows. Its removal may damage the hair follicles and eyebrows will grow poorly. Otherwise, a good aesthetic prognosis after removal with a radiofrequency knife.
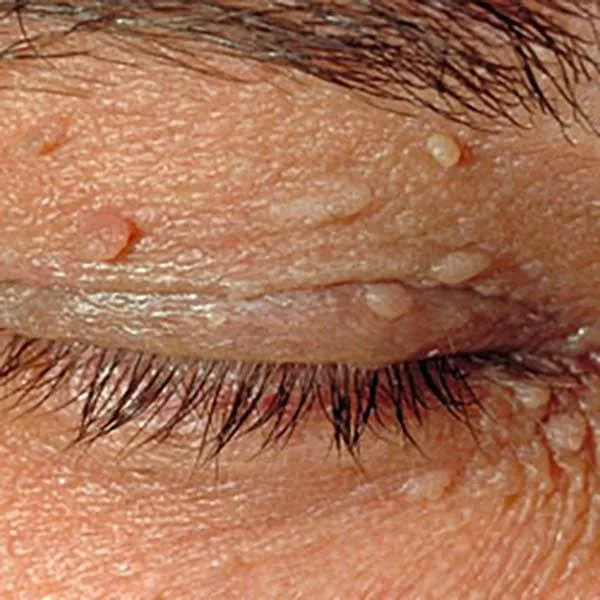
Small seborrheic moles and skin polyps on the eyelids. The changes are benign and can be easily removed with a radiofrequency knife without scars.
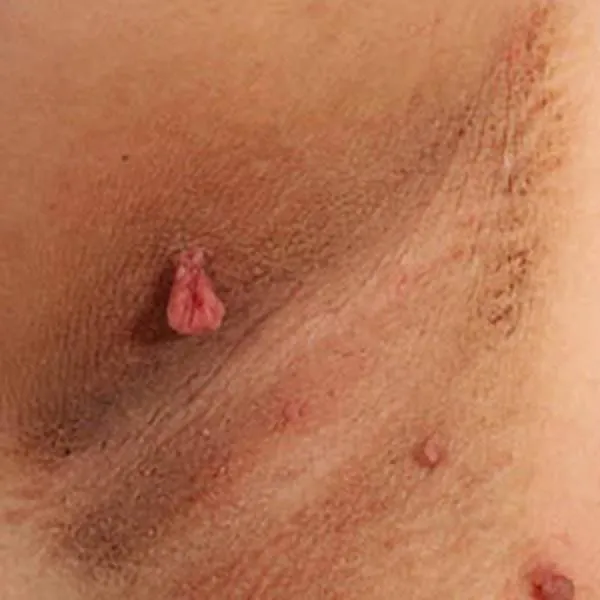
Skin polyps or papillomas in the underarm area. If they are not removed, they can become inflamed due to friction against the fabric. They can potentially be removed with a radiofrequency knife. After removal, small light spots remain.
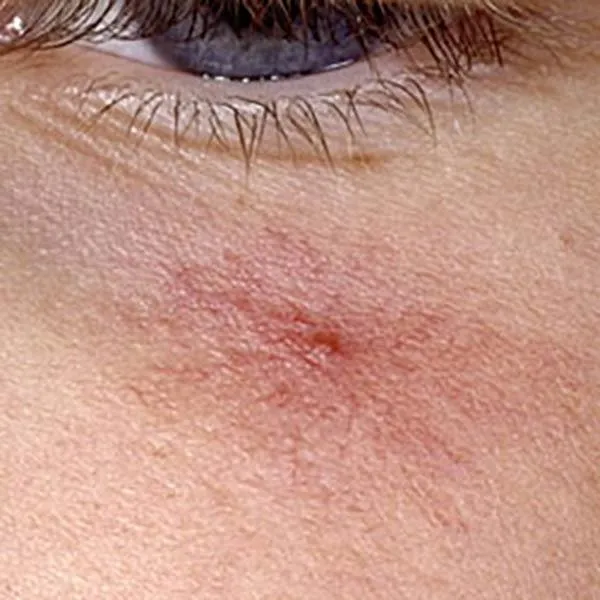
A vascular star is a benign enlargement of capillaries. It can be removed using a radiofrequency knife. Usually, there is no trace left on the face after removal.
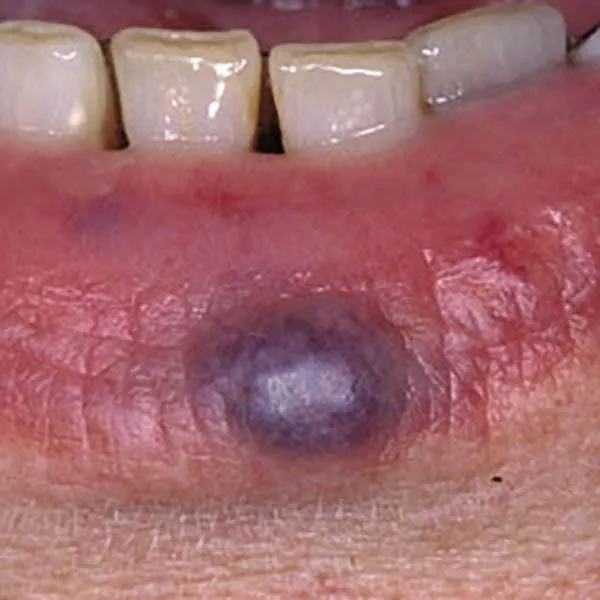
Varicose enlargement on the lips is just an aesthetic defect. It is well removed with a radiofrequency knife, a white spot may remain.
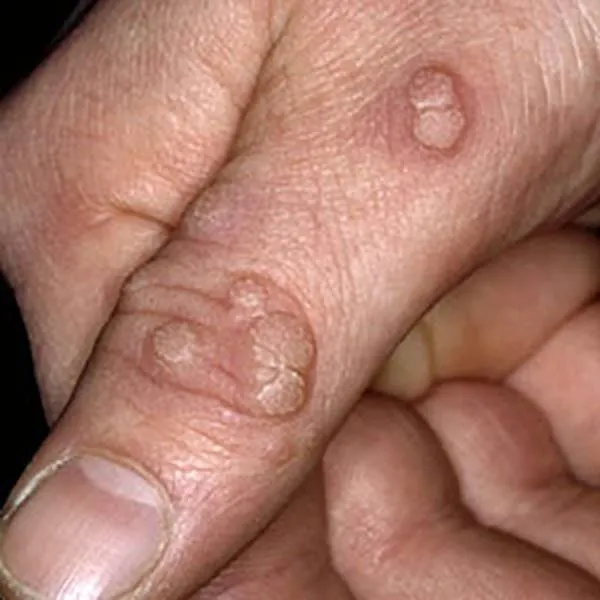
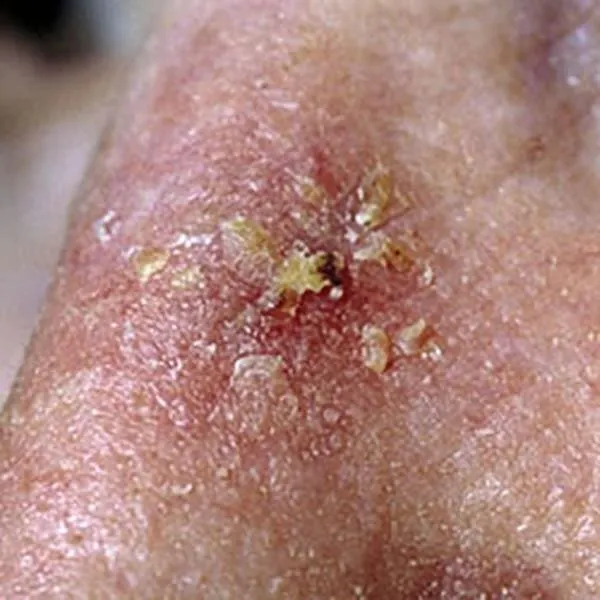
A wart on the finger is a viral disease that can go away on its own. It can be removed with a radio frequency knife, but several procedures may be required.
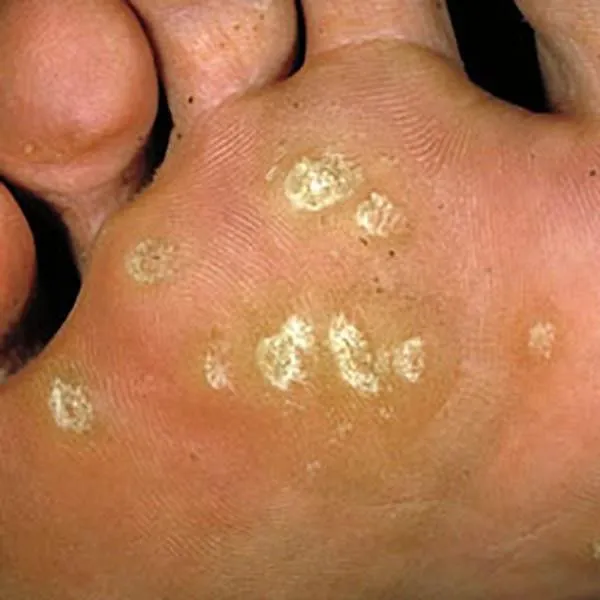
A wart on the foot that has grown into the skin and causes pain. It can be removed with a radiofrequency knife, but several procedures may be required.
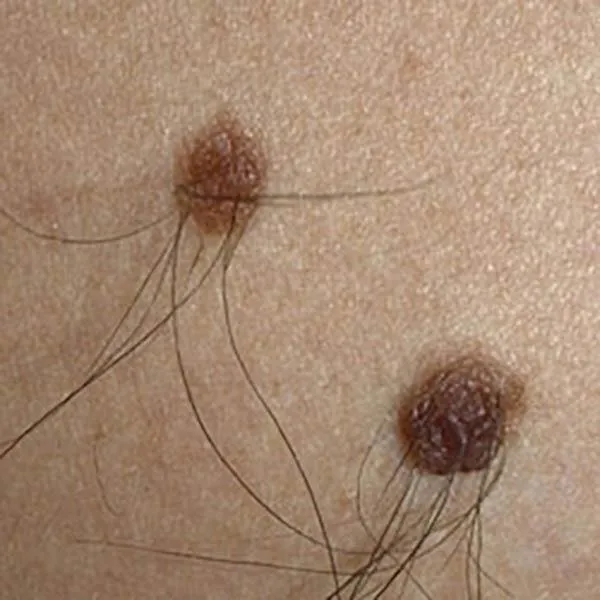
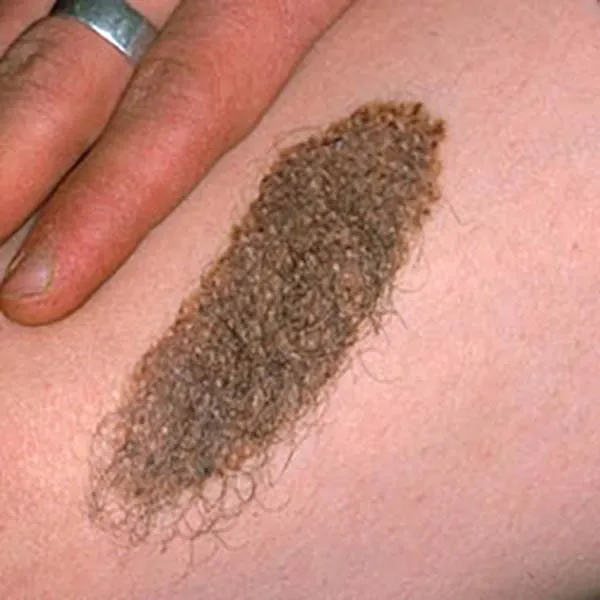
A benign intradermal mole, characterized by hair growth. It can be removed with a radiofrequency knife. Usually, there is no trace left on the face after removal, and only a light spot remains on the body and limbs. Typically, hair continues to grow even after removal.
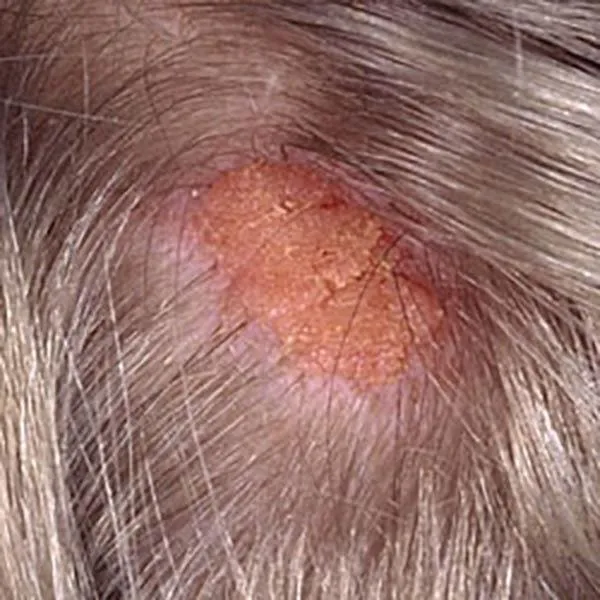
On the hairy part of the head, there is a nevus sebaceous. It appears in childhood, and hair does not grow on it. In adulthood, it can transform into a basal cell carcinoma. It is usually surgically removed at a young age. It can also be removed with a radiofrequency knife.
luomien-kuvagalleria.i2t1
luomien-kuvagalleria.i2t2
luomien-kuvagalleria.i2t3
luomien-kuvagalleria.i2t4
luomien-kuvagalleria.i2t5
luomien-kuvagalleria.i2t6
luomien-kuvagalleria.i2t7
luomien-kuvagalleria.i2t8
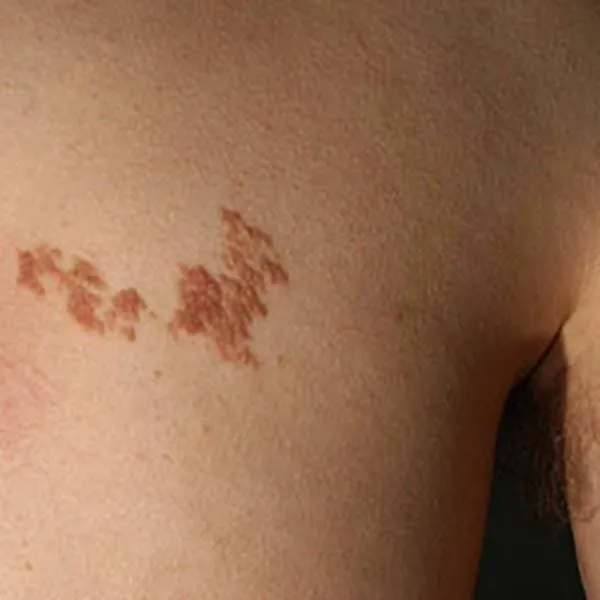
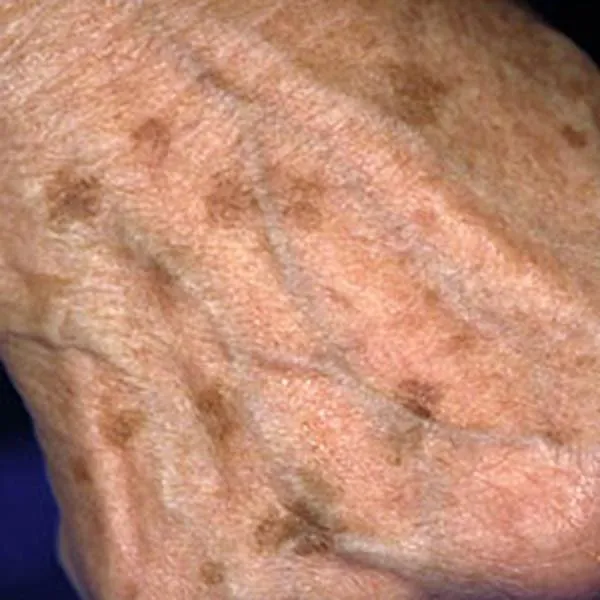
Solar keratosis is a reddish, rough skin formation that can degenerate into squamous cell skin cancer. It needs to be removed as soon as the diagnosis is made. It can be removed using a radiofrequency knife. On the face, there is usually no trace left after removal, on the body and limbs - only a light spot. If the wound does not heal after removal or the formation reappears, you should immediately consult a doctor.
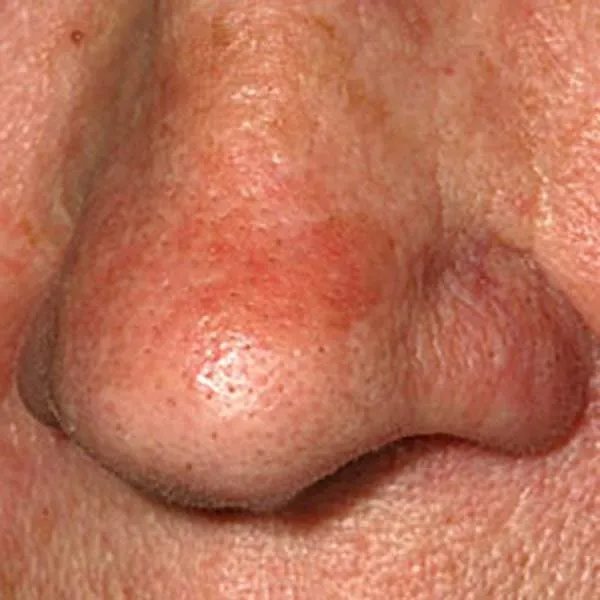
Solar keratosis on the nose is a reddish, rough skin formation that can turn into squamous cell skin cancer. It needs to be removed as soon as the diagnosis is made. It can be removed with a radiofrequency knife. On the face, there is usually no trace left after removal, on the body and limbs - only a light spot. If the wound does not heal after removal or the formation reappears, you should see a doctor immediately.
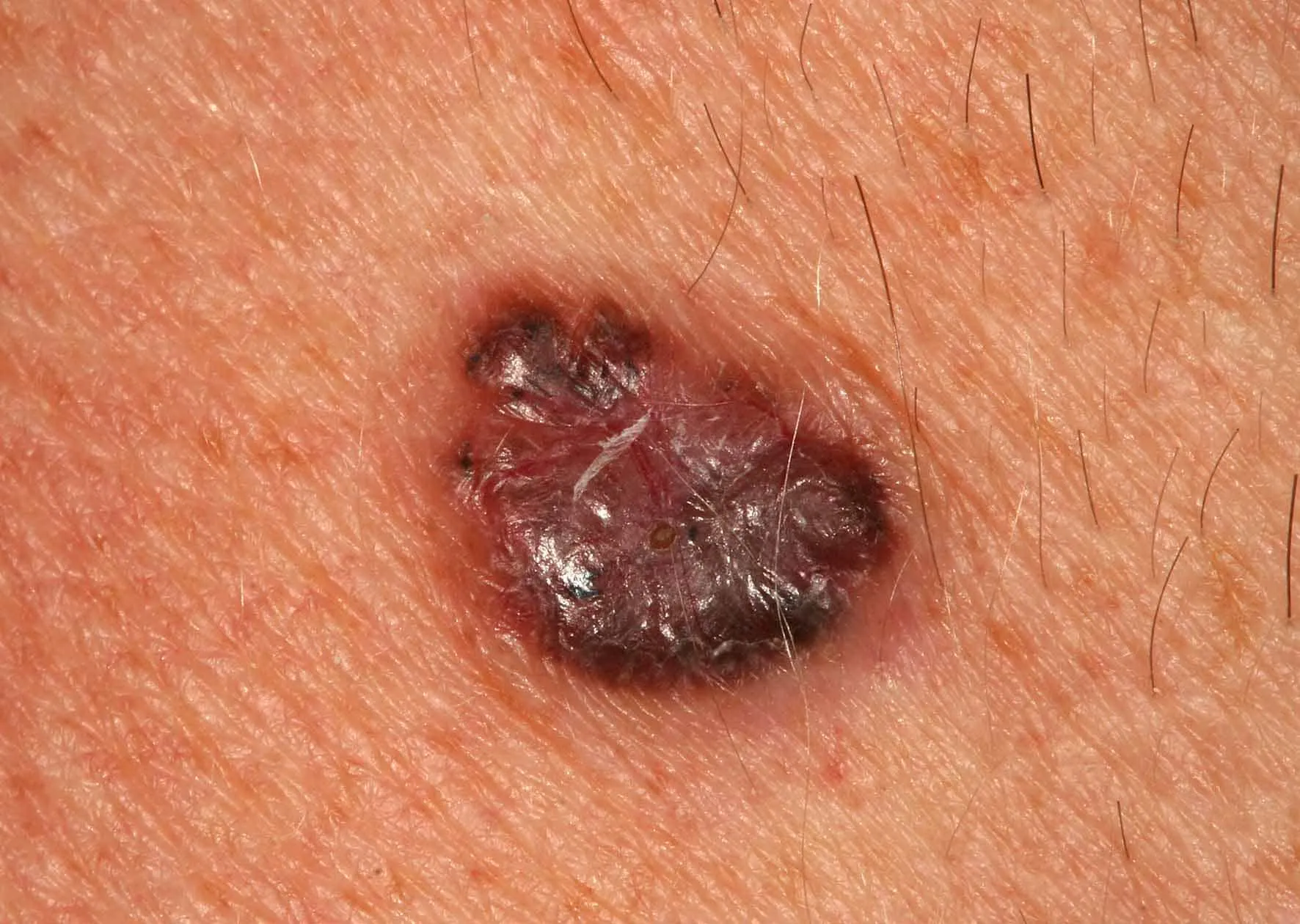
Basalioma or basal cell carcinoma. It doesn't metastasize, but it can grow deeply into other tissues. Urgent removal is necessary!
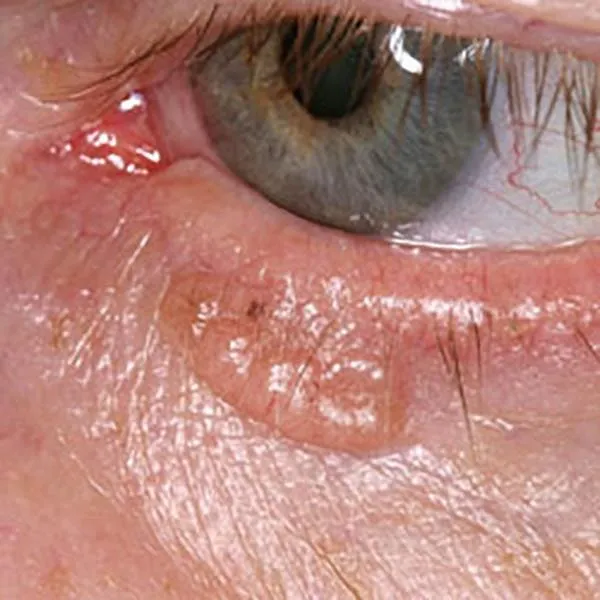
Nodular basal cell carcinoma or basal cell cancer on the lower eyelid. Urgent removal is necessary!
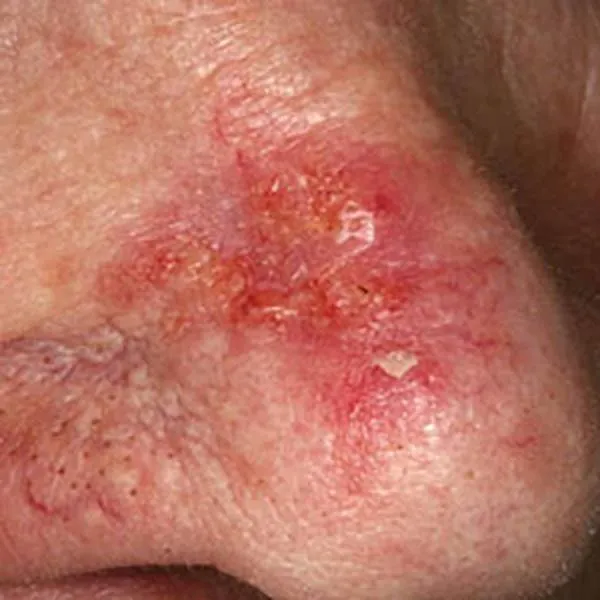
Nodular basal cell carcinoma or basal cell cancer on the nose. Urgent removal required!
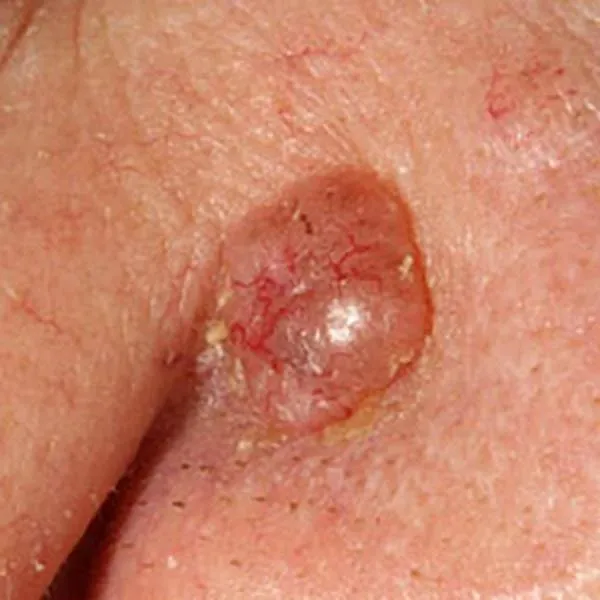
Basal cell carcinoma or basal cell cancer. Urgent removal needed!
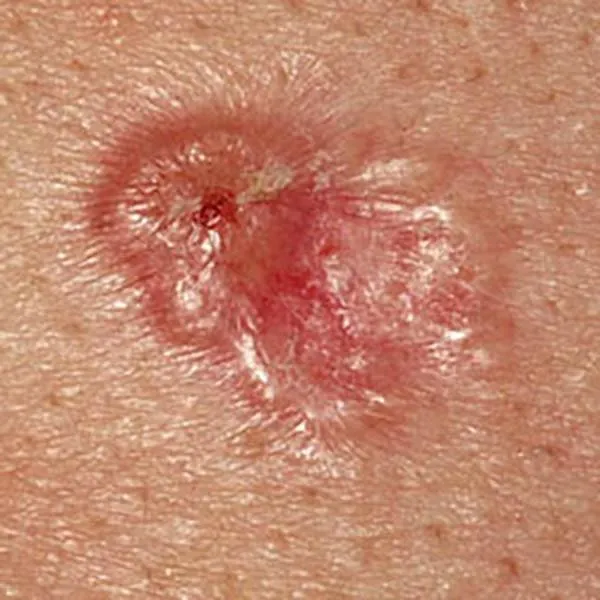
Nodular basalioma or basal cell carcinoma on the lower eyelid. Urgent removal is necessary!
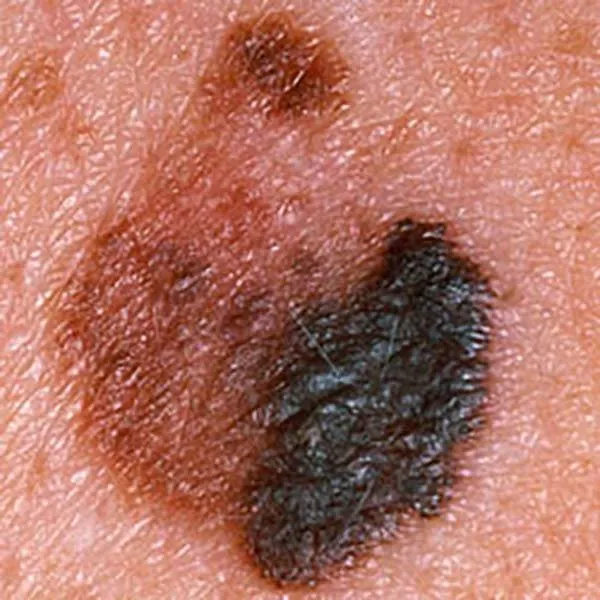
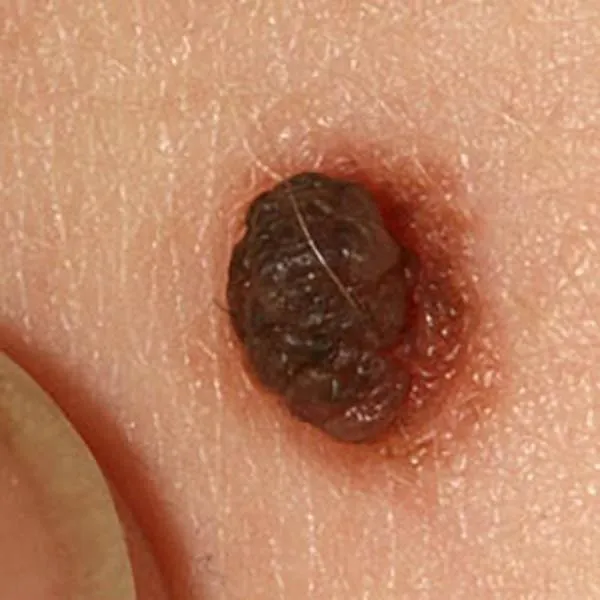
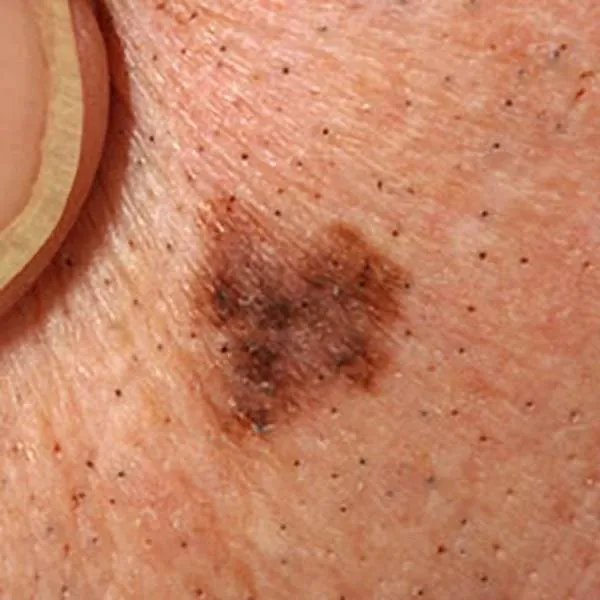
Melanoma, where asymmetric pigment is visible. Urgent referral to a university clinic for surgery.
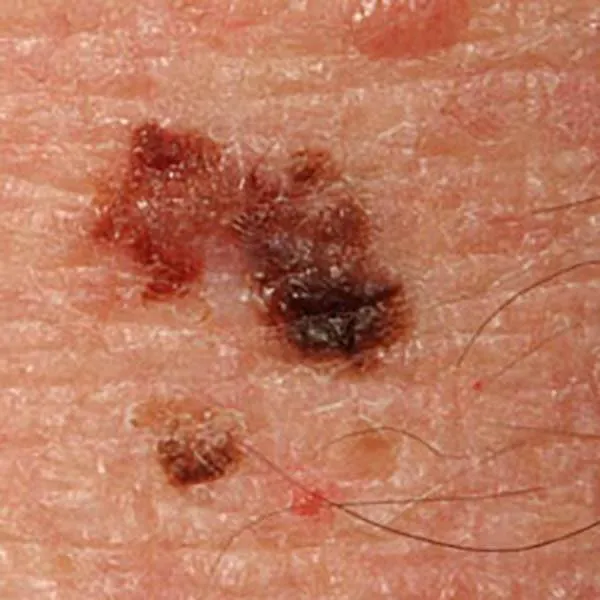
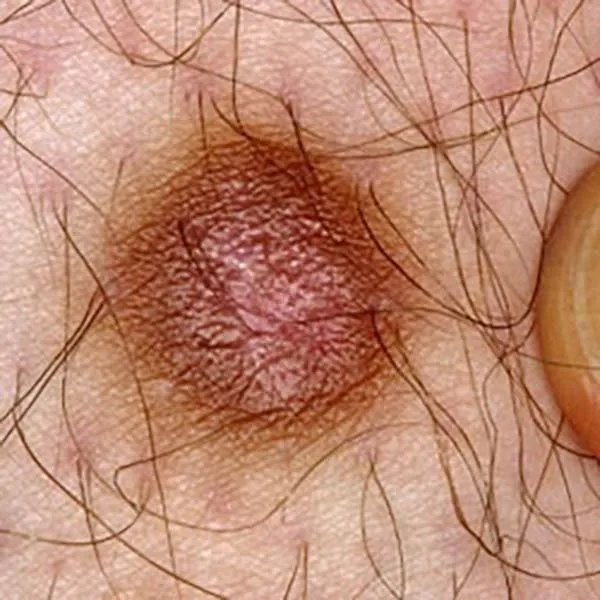
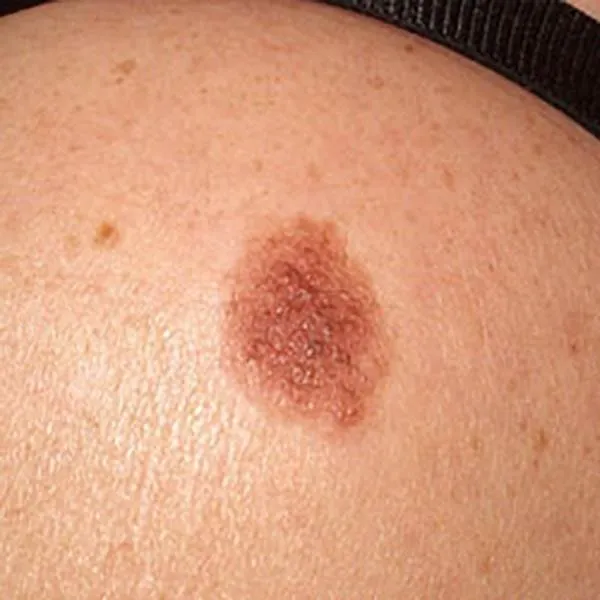
Melanoma with different shades of pigment. An urgent referral to a university clinic for treatment is needed!
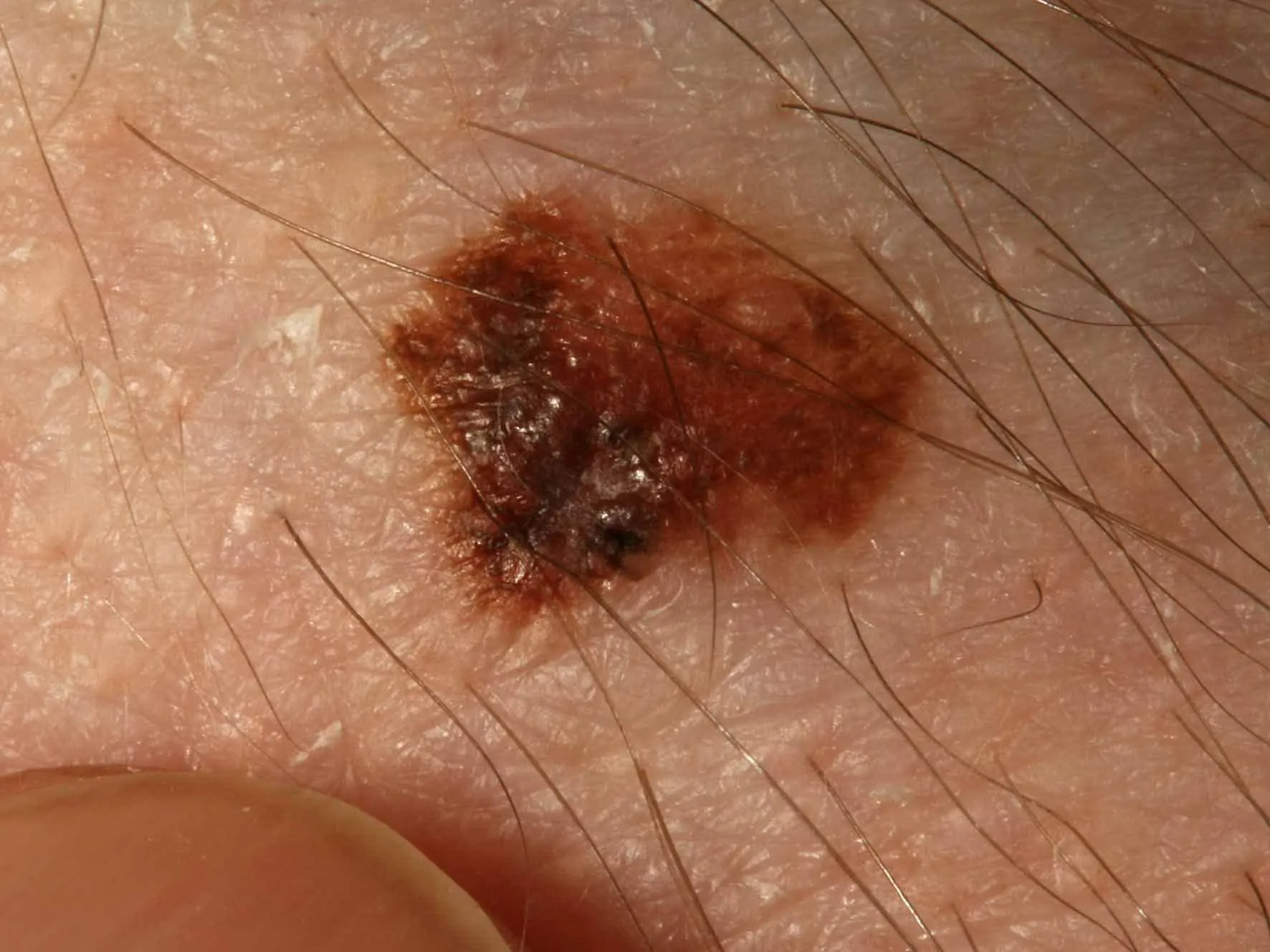
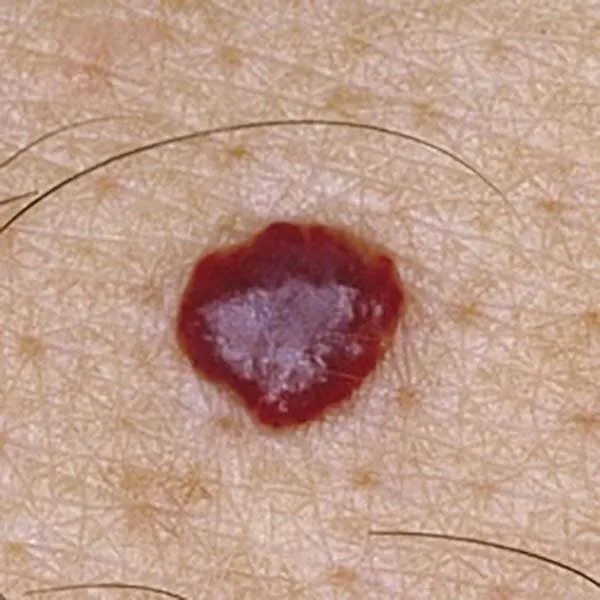
Thin melanoma of uneven color and shape. Urgent referral to the university clinic for treatment is necessary!
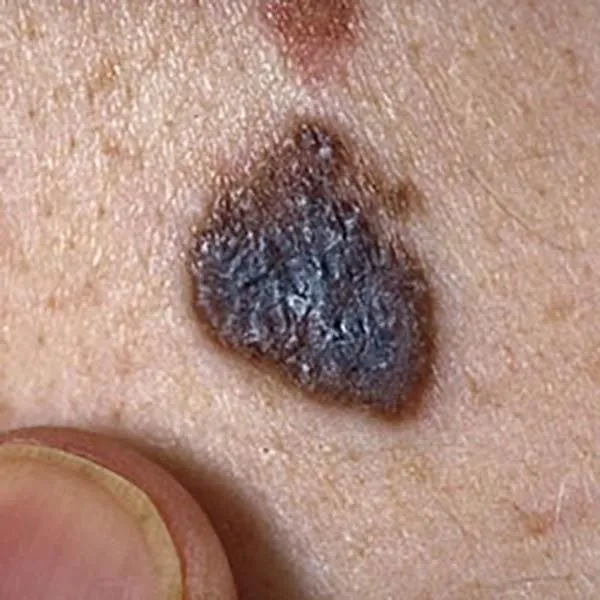
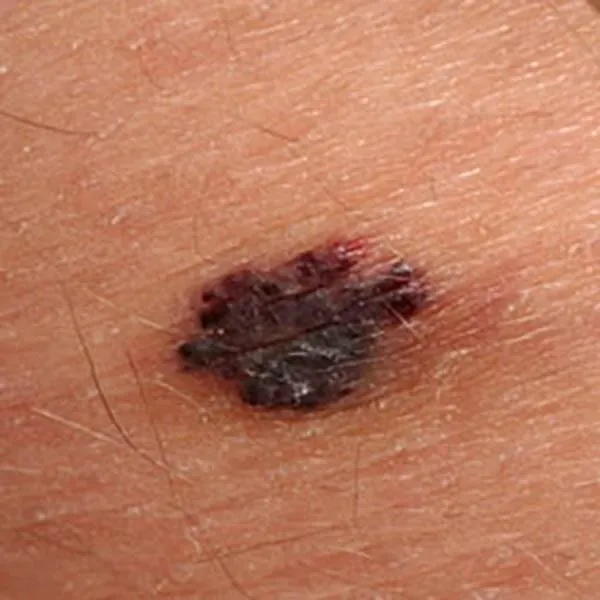
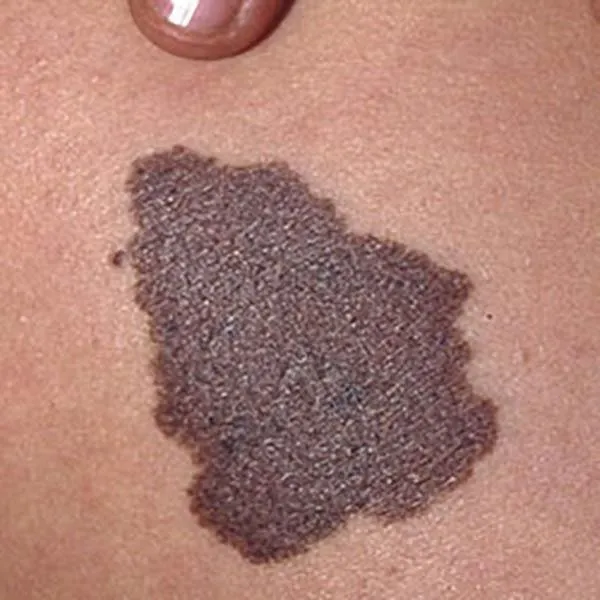
A melanoma on the body, which has a bluish tint, suggests malignancy. Immediate referral to the university clinic for treatment is needed!
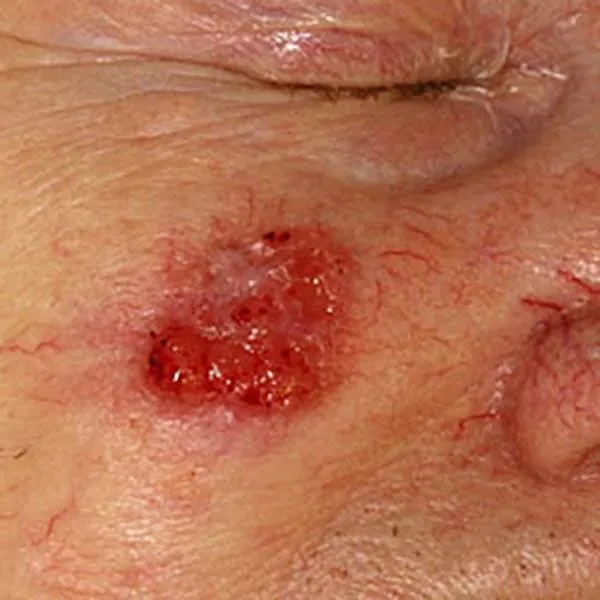
luomien-kuvagalleria.i3t12
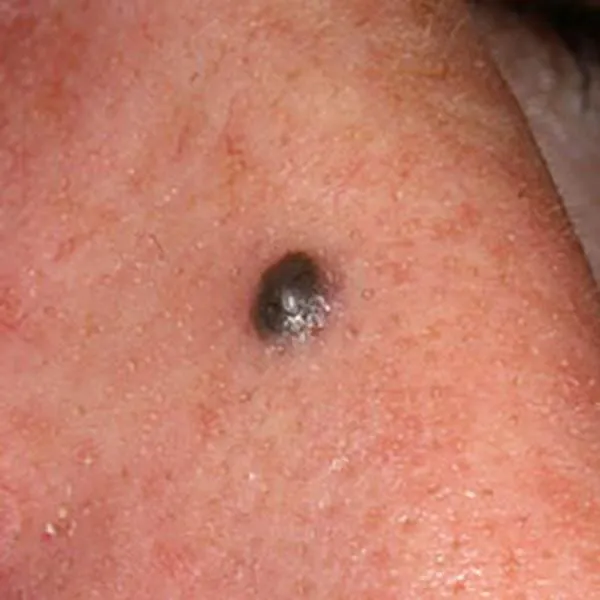
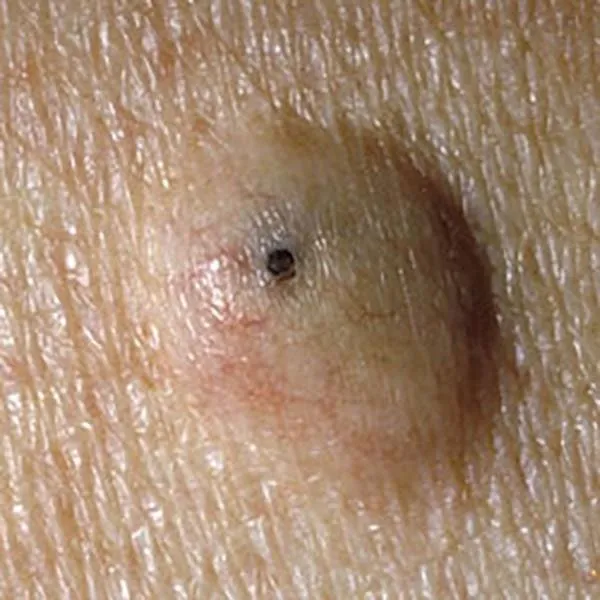
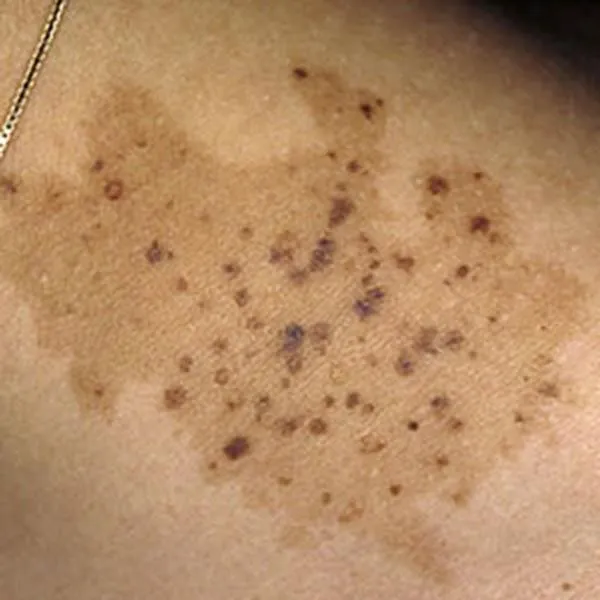
A blue nevus is a very dark birthmark, which very rarely turns malignant. A biopsy is recommended to confirm benignity.
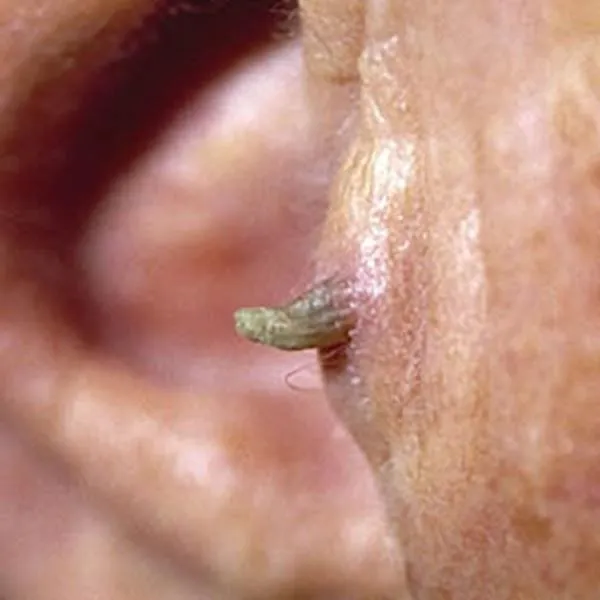
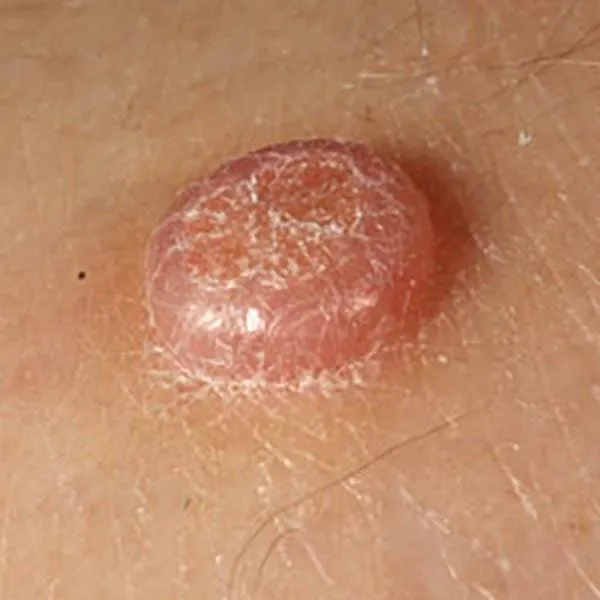
Horny keratoma, which often develops on solar keratosis. It is recommended to remove it with confirmation of its benignity by a histologist.
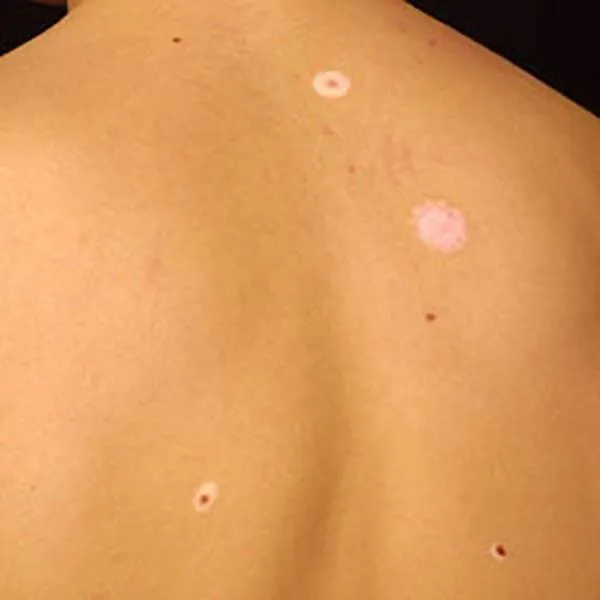
Halo nevus is an intradermal mole around which a light halo forms. The same change is possible around melanoma, therefore a biopsy is recommended.